Introduction to Autonomous Vehicle Technologies (CDIO #Assignment 2)
In this week's CDIO assignment we will look deeper into autonomous vehicles and gain some understanding about the technologies used to achieve autonomous driving.
Autonomous vehicles are packed with technology. These wide range of technologies can be divided based on their main function area. To properly understand these technology, let's first look at the normal structure of an autonomous vehicle. As a complex intelligent system, the structure of autonomous vehicle or robot are usually divided into three parts: environment detection, decision making and vehicle motion control. Based on these three parts, different technologies are investigated relating to environment sensing, localization, path planning, path following and vehicle dynamic control. Many ADAS systems and functions are a combination of several technologies.
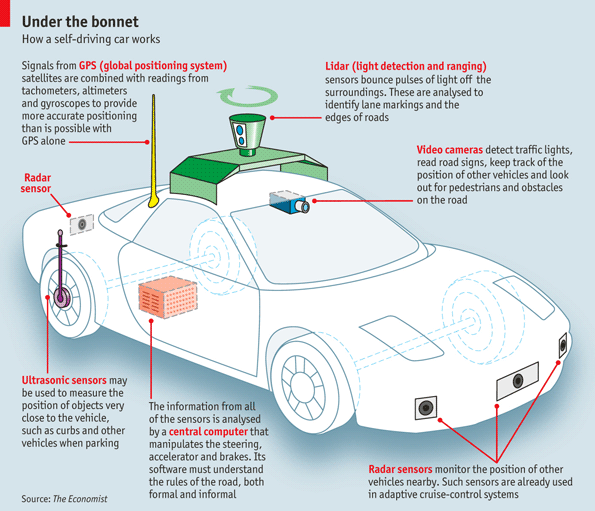
For the autonomous vehicle development nowadays, most important focus are on environment sensing, which give the control unit of intelligent enough and accurate information about surrounding environment. Lots of sensors are used to detect environment. As shown in figure 1 below, most modern sensors used for environment detection and vehicle state estimation are: GPS, Lidar, Camera, Radar, Ultrasonic sensor, and infrared sensor.
https://www.reddit.com/r/SelfDrivingCars/
Links:
http://www.aero.org/education/primers/gps/GPS-Primer.pdf
http://freegeographytools.com/2007/gps-satellite-display-in-google-earth
Links:
http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/lidar.html
http://www.lidar-uk.com/how-lidar-works/
Links:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radar
Link:
https://www.teledynedalsa.com/imaging/knowledge-center/appnotes/ccd-vs-cmos/
Link:
http://education.rec.ri.cmu.edu/content/electronics/boe/ultrasonic_sensor/1.html
Link:
http://education.rec.ri.cmu.edu/content/electronics/boe/ir_sensor/1.html
All the mentioned sensors are combined on an autonomous vehicle to perform some ADAS functions like collision warning, lane keeping or SLAM. A figure below shows the detection range and setting of sensors on the vehicles, together with the related systems they are used for.
https://www.kurumaerabi.com/car_news/info/110909/
Now let's look a little bit deeper into Lidar, which is quite popular of environment detection and mapping in autonomous vehicles.
As mentioned above, Lidar use time of filght to measure distance. Type of Lidar includes static Lidar and moving Lidar. Static Lidar emit single or multiple beams, can measure one point at a time and has no moving parts;
Moving Lidar, which is usually rotational Lidar, has a motor and an encoder to measures rotation angle and scans at a certain frequency.
Compared with Radar and other distance measuring sensors, Lidar has higher accuracy, and better angular resolution. It is also faster in getting the data, and have higher data density.
The drawbacks are that the lidar is far more expensive than other sensors. It may have some weather issues during bad weather. Also it can be relative big and has some packaging problems.
Future potential use of Lidar:
The use and demand for LiDAR is increasing on a daily basis today. Users not only have access to digital elevation maps, but also 3-D battlespace characterization, intelligence and situational awareness. With these kind of more specific environment information, we can form the 3D map and use Lidar to support mission planning, local awareness, forensics, target tracking, and pilot hazard detection and avoidance.
Links:
http://www.kmimediagroup.com/geospatial-intelligence-forum/magazines/296-gif-2011-volume-9-issue-1-february/3841-lidar-future-sp-568#sthash.LbmKulCQ.dpuf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lidar
http://gisgeography.com/lidar-light-detection-and-ranging/
Autonomous vehicles are packed with technology. These wide range of technologies can be divided based on their main function area. To properly understand these technology, let's first look at the normal structure of an autonomous vehicle. As a complex intelligent system, the structure of autonomous vehicle or robot are usually divided into three parts: environment detection, decision making and vehicle motion control. Based on these three parts, different technologies are investigated relating to environment sensing, localization, path planning, path following and vehicle dynamic control. Many ADAS systems and functions are a combination of several technologies.
For the autonomous vehicle development nowadays, most important focus are on environment sensing, which give the control unit of intelligent enough and accurate information about surrounding environment. Lots of sensors are used to detect environment. As shown in figure 1 below, most modern sensors used for environment detection and vehicle state estimation are: GPS, Lidar, Camera, Radar, Ultrasonic sensor, and infrared sensor.
https://www.reddit.com/r/SelfDrivingCars/
- GPS: GPS is the global positioning system, which uses 24(+6) satellites around earth to provide the real-time position of the connected item. GPS system can have time accuracy of about 3ns. Although GPS may have some data error due to exist of atmosphere, we can use Differential GPS technology to increase accuracy. However, vehicles systems can still usually lose GPS signals in tunnels or among mountains.
Links:
http://www.aero.org/education/primers/gps/GPS-Primer.pdf
http://freegeographytools.com/2007/gps-satellite-display-in-google-earth
- Lidar: Lidar is Light Detection And Ranging which use light emission and time of flight to give distance information. The Lidar usually has an emitter and a receiver.
Links:
http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/lidar.html
http://www.lidar-uk.com/how-lidar-works/
- Radar: Radio Detection And Ranging. Radar creates radio waves and transmit it to measure distance information. Reflections of radio are received and interpreted. Higher the radio frequency is, the more narrow beam it will have, which gives a better angle separation Normal distance of Radar is up to 150-200 m. Radar can have a better accuracy without effect of weather, however, it is not very good for object classification when detecting environment.
Links:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radar
- Camera: video cameras are usually used for computer vision based detection system. With fast development of image processing technologies, computer can easily use the images from camera to detect and track other vehicles, recognize road lines and signs, and also avoid collision of passengers. Basic type of cameras includes CMOS and CCD.
Link:
https://www.teledynedalsa.com/imaging/knowledge-center/appnotes/ccd-vs-cmos/
- Ultrasonic sensor: An Ultrasonic sensor is a device that can measure the distance to an object by using sound waves. It measures distance by sending out a sound wave at a specific frequency and listening for that sound wave to bounce back. By recording the elapsed time between the sound wave being generated and the sound wave bouncing back, it is possible to calculate the distance between the sonar sensor and the object.
Link:
http://education.rec.ri.cmu.edu/content/electronics/boe/ultrasonic_sensor/1.html
- Infrared sensor: IR Sensors work by using a specific light sensor to detect a select light wavelength in the Infra-Red (IR) spectrum. By using an LED which produces light at the same wavelength as what the sensor is looking for, you can look at the intensity of the received light. When an object is close to the sensor, the light from the LED bounces off the object and into the light sensor.
Link:
http://education.rec.ri.cmu.edu/content/electronics/boe/ir_sensor/1.html
All the mentioned sensors are combined on an autonomous vehicle to perform some ADAS functions like collision warning, lane keeping or SLAM. A figure below shows the detection range and setting of sensors on the vehicles, together with the related systems they are used for.
https://www.kurumaerabi.com/car_news/info/110909/
Now let's look a little bit deeper into Lidar, which is quite popular of environment detection and mapping in autonomous vehicles.
As mentioned above, Lidar use time of filght to measure distance. Type of Lidar includes static Lidar and moving Lidar. Static Lidar emit single or multiple beams, can measure one point at a time and has no moving parts;
Static Lidar
Moving Lidar, which is usually rotational Lidar, has a motor and an encoder to measures rotation angle and scans at a certain frequency.
Moving Lidar
Modern vehicles use rotational lidar either on top of the vehicle or on corners of front to scan the environment and get quite accurate distance information about surroundings. These information can be used for emergency braking, pedestrian detection and collision avoidance. More importantly, Lidar is often used for SLAM (Simultaneous localization and mapping), which can give the the vehicle state information and build the real-time map at the same time.Compared with Radar and other distance measuring sensors, Lidar has higher accuracy, and better angular resolution. It is also faster in getting the data, and have higher data density.
The drawbacks are that the lidar is far more expensive than other sensors. It may have some weather issues during bad weather. Also it can be relative big and has some packaging problems.
Future potential use of Lidar:
The use and demand for LiDAR is increasing on a daily basis today. Users not only have access to digital elevation maps, but also 3-D battlespace characterization, intelligence and situational awareness. With these kind of more specific environment information, we can form the 3D map and use Lidar to support mission planning, local awareness, forensics, target tracking, and pilot hazard detection and avoidance.
Links:
http://www.kmimediagroup.com/geospatial-intelligence-forum/magazines/296-gif-2011-volume-9-issue-1-february/3841-lidar-future-sp-568#sthash.LbmKulCQ.dpuf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lidar
http://gisgeography.com/lidar-light-detection-and-ranging/



Please try to find the actual image link (not just a reddit link).
ReplyDeleteExcellent work on LIDAR and its future applications.
- The CDIO Academy Team